Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
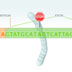
A single nucleotide polymorphism, or SNP, occurs when two individuals in the population differ by a single letter in the DNA sequence.
A single nucleotide polymorphism, or SNP, occurs when two individuals in the population differ by a single letter in the DNA sequence.
The genetics of cognitive disorders is complex because diseases like schizophrenia or autism are associated with multiple genes. The genomic code is a long sequence written in only four letters – A,G,T, and C, which correspond to Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine. A single nucleotide polymorphism, or SNP, occurs when two individuals in the population differ by a single letter in the DNA sequence. For instance, one individual may have a ‘G’ at this position, and another individual may have a ‘C.’ Changes in the DNA sequence can lead to changes in a gene’s biological function. For example, a change in the DNA sequence can lead to a change in the sequence of the protein that is produced, or it may cause a protein to terminate prematurely.